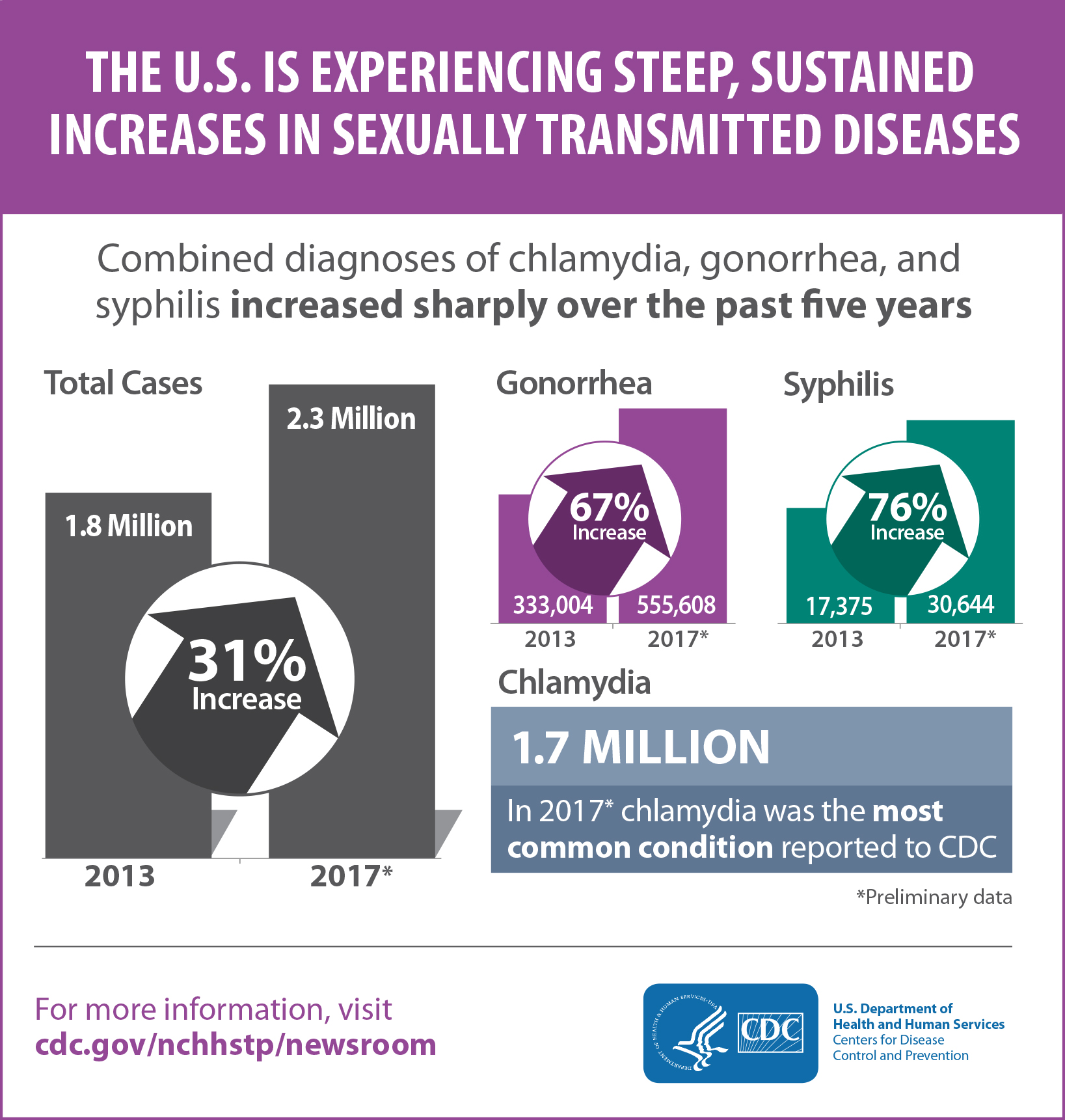
Nearly 2.3 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis were diagnosed in the United States in 2017, according to preliminary data released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) at the National STD Prevention Conference in Washington, D.C..
This surpassed the previous record set in 2016 by more than 200,000 cases and marked the fourth consecutive year of sharp increases in these sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
(The CDC reports that cases of sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis reached an all-time high in 2016 – Which has now been surpassed in 2017. But who or what is to blame for the rising STD numbers? Courtesy of Fox News and YouTube. Posted on Sep 27, 2017.)
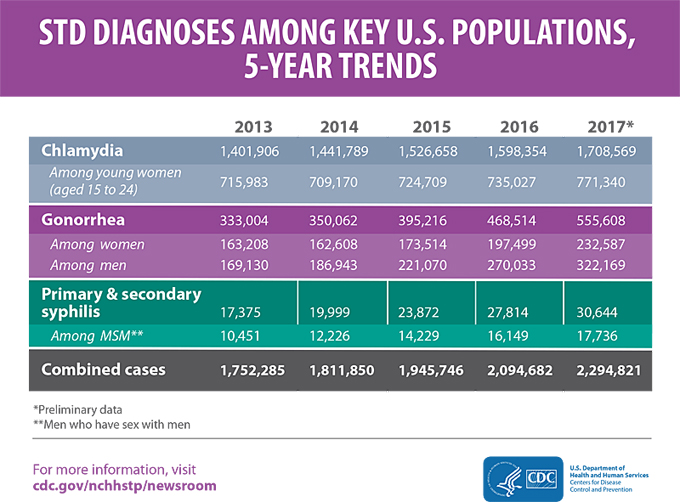
The CDC analysis of STD cases reported for 2013 and preliminary data for 2017 shows steep, sustained increases:
-
Gonorrhea
- Gonorrhea diagnoses increased 67 percent overall (from 333,004 to 555,608 cases according to preliminary 2017 data) and nearly doubled among men (from 169,130 to 322,169).
- Increases in diagnoses among women — and the speed with which they are increasing — are also concerning, with cases going up for the third year in a row (from 197,499 to 232,587).
-
Primary and secondary syphilis
- Syphilis diagnoses increased 76 percent (from 17,375 to 30,644 cases).
- Gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (MSM) made up almost 70 percent of primary and secondary syphilis cases where the gender of the sex partner is known in 2017.
- Primary and secondary syphilis are the most infectious stages of the disease.
-
Chlamydia
- Chlamydia remained the most common condition reported to CDC.
- More than 1.7 million cases were diagnosed in 2017, with 45 percent among 15- to 24-year-old females.
“We are sliding backward,” said Jonathan Mermin, M.D., M.P.H, director of CDC’s National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention.

“It is evident the systems that identify, treat, and ultimately prevent STDs are strained to near-breaking point.”
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis are curable with antibiotics, yet most cases go undiagnosed and untreated — which can lead to severe adverse health effects that include infertility, ectopic pregnancy, stillbirth in infants, and increased HIV risk.
Prior studies suggest a range of factors may contribute to STD increases, including socioeconomic factors like poverty, stigma, and discrimination; and drug use.

Continued concerns about antibiotic resistant gonorrhea
The threat of untreatable gonorrhea persists in the United States, and reports of antibiotic resistant gonorrhea abroad have only reinforced those concerns.
Over the years, gonorrhea has become resistant to nearly every class of antibiotics used to treat it, except to ceftriaxone, the only remaining highly effective antibiotic to treat gonorrhea in the United States.
In 2015, CDC began recommending health care providers prescribe a single shot of ceftriaxone accompanied by an oral dose of azithromycin to people diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Azithromycin was added to help delay the development of resistance to ceftriaxone.
(This animation details the history of drug-resistant gonorrhea in the United States, the dangers of untreatable gonorrhea, and why this issue must remain a top public health priority. Courtesy of Fox News and YouTube. Posted on May 30, 2017.)
Emerging resistance to ceftriaxone has not been seen since the dual therapy approach was implemented, and there has not yet been a confirmed treatment failure in the United States when using this recommended therapy.
New CDC findings, however, show that emerging resistance to azithromycin is now on the rise in laboratory testing — with the portion of samples that showed emerging resistance to azithromycin increasing from 1 percent in 2013 to more than 4 percent in 2017.
The finding adds concerns that azithromycin-resistant genes in some gonorrhea could crossover into strains of gonorrhea with reduced susceptibility to ceftriaxone — and that a strain of gonorrhea may someday surface that does not respond to ceftriaxone.

















