By Kevin Buxton, Director of Business Development at FLIR Systems
Radiation is one of the most dangerous threats to responders. You can’t see it, smell it or hear it.
It could be part of an attack, or it may be a benign radiation source.
Fast, informed decision-making is critical when lives are on the line – having the right tools in your toolkit can make all the difference.
No one radiation instrument can meet all the demands that a responder may encounter, and a good deployment platform relies on having a range of supporting technologies.
Deciding what tools to arm yourself with can seem complicated, but it doesn’t have to be.
(Radiation is not well understood. FLIR PRIMED’s Grant Coffey covers the important safety basics you need to know. FLIR PRIMED is FLIR’s 2017 ‘ASTORS’ Award-Winning CBRNE Training Video Series. Every few weeks, they deliver best practices, industry insights, and real-life experiences to help you stay prepared. Each episode is accompanied by a field checklist or downloadable guide that you can use right now! See more at FLIR.com/PRIMED Courtesy of FLIR Systems and YouTube. Posted on Apr 14, 2017.)
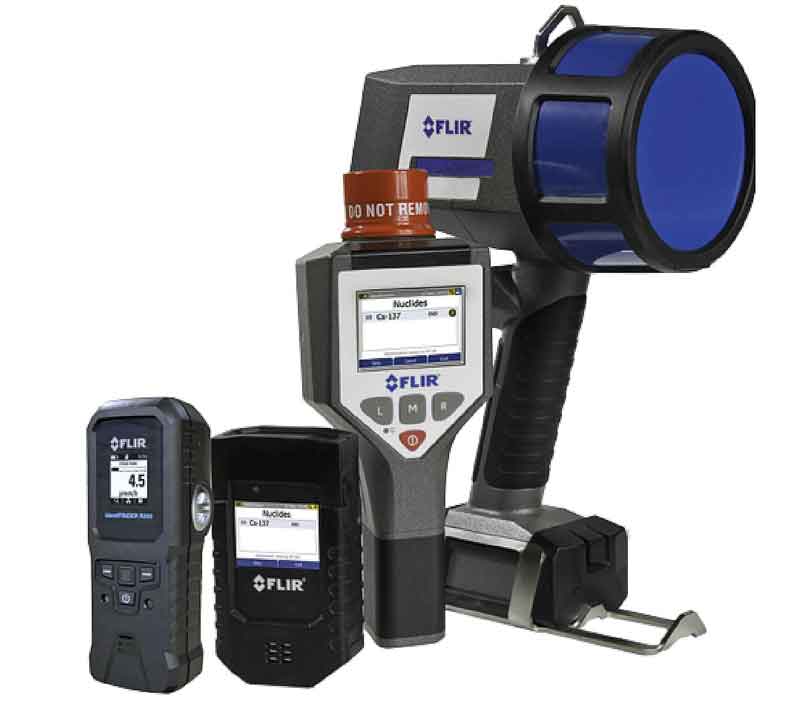
TYPES OF HANDHELD INSTRUMENTS
There are several types of handheld radiation detection instruments that can be considered, including:
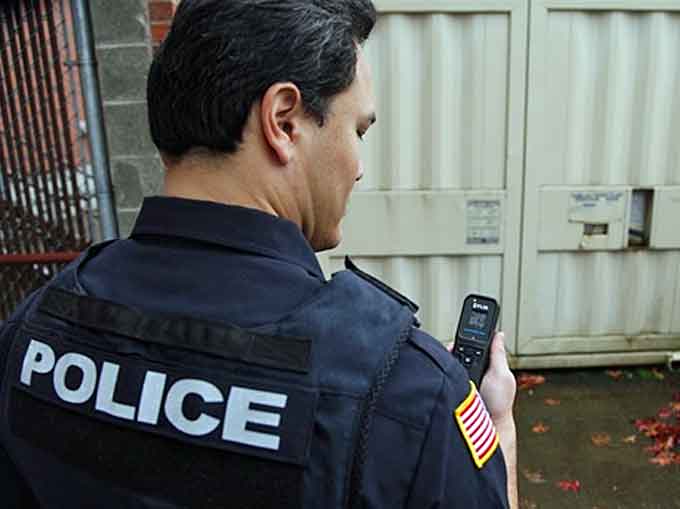
Personal Survey Meter/Personal Radiation Detector (PSM/PRD)
-
The most widely deployed type of radiation detector, PRDs are belt-worn devices that form the frontline for threat interdiction, offering first responders, or security personnel, the knowledge they need of their surroundings to ensure their personal protection.

-
However, they require the support of more capable instruments once the initial detection has been made.
-
Additional tools are needed to perform identification once the initial detection has been made.
Spectroscopic Personal Radiation Detector (SPRD)
-
SPRD can be belt-worn or vehicle-mounted to function as a PRD.
-
Additionally, they provide real-time spectroscopic capability for monitoring gamma and/or neutron activity, performing isotope identification, enhancing on-scene information, and safer decision-making on-scene during a radiological event.
Radionuclide Identification Device (RID)
-
RID Handheld devices that are most often used on the front line or for secondary verification on-scene.
-
RIDs are generally more sensitive than PSM/PRDs and SPRDs due to their use of crystalline scintillation or semiconductor detector materials.
-
They are considered the best all-purpose survey tool for gamma and/or neutron radiation, and they generate the spectroscopic info needed to identify specific nuclides.
(FLIR identiFINDER R200 with neutron capability is an important early warning system for responders, and a 2017 ‘ASTORS’ Homeland Security Award Winner. Courtesy of FLIR Systems and YouTube. Posted on Nov 17, 2015.)
CONSIDERATIONS AND DEPLOYMENT SCENARIOS
Some key considerations that should be addressed in deciding what set of complementary tools to include in your deployment strategy, include:
-
Technologies: Tube-based or crystal-based
-
Potential applications: Surveying, front-line, or secondary confirmation
-
Sensitivity: Monitoring or “search and find”
-
Resolution: Separating malicious from benign substances

-
Reachback: Sending information back from the front-line
-
Field Ruggedness: Surviving harsh environments
-
Neutron Detection: Early warning for malicious materials
One of the best ways to start thinking through your deployment plan is by reviewing these considerations in terms of the missions and scenarios you expect to encounter.
Here are some things to keep in mind for common scenarios.
Scenario #1: Monitoring pedestrian flow at events, entrances, or other checkpoints, where the mission is to locate, identify, and separate innocent or benign sources (medical patients) from potential threats.
(Radiation events are rare but extremely serious – understanding the tools available to you and how they work could make all the difference. See FLIR Primed discussed time, distance, and shielding. In Episode 27, they take a deeper look into sensitivity and resolution – two important factors that determine how quickly and cleanly a detector will sense and identify a radiation source. Courtesy of FLIR Systems and YouTube. Posted on Dec 18, 2018.)
Considerations:
-
There is a control of flow and it can be stopped or started as needed.
-
Devices with smaller detectors will not overload if a medical patient passes through.
-
Devices with smaller detectors will not detect sources too distant to physically locate.
-
The identification-capable devices will allow immediate adjudication of the radiological event.
-
The belt-wearable options leave both hands free to perform tasks.
-
Devices with a neutron detection option add a layer of protection on the frontline.

Scenario #2: Screening vehicles rather than pedestrians, as well as larger volumes, such as shipping containers, semi-trucks, and other cargo.
-
All devices should be considered to form layers of capability.
-
Smaller detectors form excellent front-line detection.
-
Larger detectors provide additional support, detect the presence of radiation earlier, deliver increased sensitivity, and can identify more quickly if needed.
-
Higher sensitivity improves the speed of initial detection.
-
Faster identification and adjudication help maintain flow at check-point or loading dock.
-
Devices with a neutron detection option add a layer of protection.

Larger volumes (shipping containers, semi-trucks, and containers) provide the opportunity for creative concealment methods (shielding and masking), where a higher resolution device will provide more fidelity and improve the ability to identify both present materials and artifacts.
Additionally, higher resolution combined with a larger detector provides even faster identification.
In all scenarios, there is a great benefit in deploying the maximum number of detectors to increase the tightness of the net in place.
The right balance of initial detection and adjudication devices can greatly increase the effectiveness of security operation.
(See the FLIR identiFINDER R440 in action – a lightweight, sourceless RIID that can be operated with one hand and is IP67-rated to survive tough missions. Courtesy of FLIR Systems and YouTube. Posted on Oct 23, 2017.)
NEUTRON CAPABILITY
Some of these considerations are easier to answer than others. One that can sometimes be confusing is determining if you need neutron detection capability in your toolkit.
The desire to monitor for the presence of neutrons is usually driven by two main considerations:

-
Neutrons have the ability to penetrate material and travel distances far greater than any other form of radiation.
-
A neutron detector has a better opportunity of detecting neutrons before any other associated type of radiation, like gamma, from the same source.
-
The neutron detector is considered by many to be an important early warning system for the detection of malicious material.
-
-
Neutrons are often associated with the presence of fissile material. They are absolute secondary confirmation when a gamma-based identification of uranium or plutonium has been made.
-
The presence of neutrons when a non-fissile identification is made can indicate that malicious materials are being hidden or masked behind a larger benign source.
-
This is a highly suspicious situation and triggers an immediate response.
-
Most handheld RID devices are used as a stand-alone solution and the majority of those deployed have neutron detection capability.

Although neutron capability is commonly available, it is possible to buy RIDs without this option.
Belt-worn PSM and PRD devices generally do not have neutron capability due to size and cost considerations.
SPRD devices are available with or without neutron detectors, which enables customers to determine a balance point on deployment coverage, capability, and cost.
Neutron detection can be accomplished using several different detection materials, three of which are Helium-3 (He-3 Tube), zinc sulfide (ZnS), and sodium iodide doped with lithium (NaIL).

PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER
These are just a few of the key points to consider when building out your radiation detection deployment strategy.
Regardless of the tools you choose, proper initial training and refresher exercises are vital in making sure your team is prepared to understand alerts and how to react appropriately to malicious materials.
Remember, one size does not fit all.
Different types and sizes of detectors complement one another during a radiological event and provide a greater level of safety.
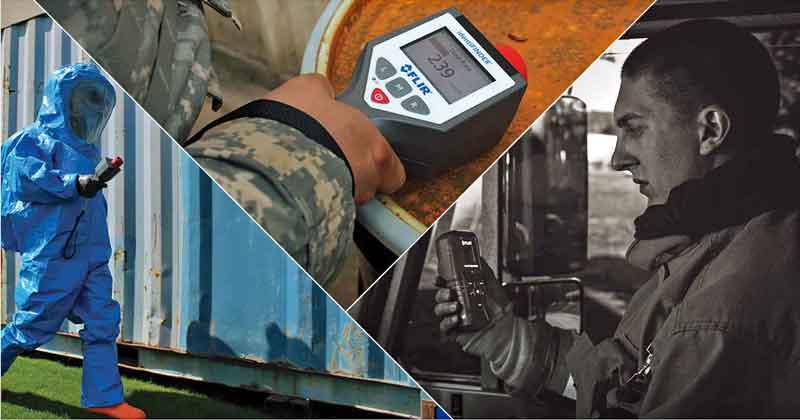

A deployment strategy should include a mix of PSMs/PRDs, SPRDs, and RIDs. Programs that incorporate a mix gain these key operational advantages:
-
Immediate access to information on the type of radiological event enhances the safety of the frontline responder
-
Reachback-enabled devices provide information to secondary responders dispatched to support the event
-
Spectroscopic information shared with decision makers beyond the frontline enables the mobilization of appropriate resources
Keep in mind the types of scenarios that you could encounter, along with some key considerations like, sensitivity, resolution, reachback and neutron detection, when determining the right mix of instruments for your toolkit.
(FLIR PRIMED Grant’s Lessons Learned: Ten of the most common mistakes Grant has seen responders make on-scene and how you can avoid them. Courtesy of FLIR Systems and YouTube. Posted on Oct 23, 2017.)
FLIR Systems Recognized in Third Annual ‘ASTORS’ Homeland Security Awards Program
FLIR Systems
-
Best Perimeter Protection Solution
-
FLIR Saros Dome Camera
-
FLIR is also a 2017 ‘ASTORS’ Awards Winner
The Annual ‘ASTORS’ Awards Program is specifically designed to honor distinguished government and vendor solutions that deliver enhanced value, benefit and intelligence to end users in a variety of government, homeland security and public safety vertical markets.

The 2018 ‘ASTORS’ Awards Program drew an overwhelming response from industry leaders with a record high number of corporate and government nominations received, as well as record breaking ‘ASTORS’ Presentation Luncheon Attendees, with top firms trying to register for the exclusive high – end luncheon and networking opportunity – right up to the event kickoff on Wednesday afternoon, at the ISC East registration!
Over 130 distinguished guests representing National, State and Local Governments, and Industry Leading Corporate Firms, gathered from across North America, Europe and the Middle East to be honored among their peers in their respective fields which included:
- The Department of Homeland Security
- The Federal Protective Service (FPS)
- Argonne National Laboratory
- The Department of Homeland Security
- The Department of Justice
- The Security Exchange Commission Office of Personnel Management
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection
- Viasat, Hanwha Techwin, Lenel, Konica Minolta Business Solutions, Verint, Canon U.S.A., BriefCam, Pivot3, Milestone Systems, Allied Universal, Ameristar Perimeter Security and More!
The Annual ‘ASTORS’ Awards is the preeminent U.S. Homeland Security Awards Program highlighting the most cutting-edge and forward-thinking security solutions coming onto the market today, to ensure our readers have the information they need to stay ahead of the competition, and keep our Nation safe – one facility, street, and city at a time.
The 2018 ‘ASTORS’ Homeland Security Awards Program was Proudly Sponsored by ATI Systems, Attivo Networks, Automatic Systems, Desktop Alert, and Royal Holdings Technologies.
Early Bird Nominations are now being accepted for the 2019 ‘ASTORS’ Homeland SecurityAwards at https://americansecuritytoday.com/ast-awards/.
Comprehensive List of Categories Include:
| Access Control/ Identification | Personal/Protective Equipment | Law Enforcement Counter Terrorism |
| Perimeter Barrier/ Deterrent System | Interagency Interdiction Operation | Cloud Computing/Storage Solution |
| Facial/IRIS Recognition | Body Worn Video Product | Cyber Security |
| Video Surveillance/VMS | Mobile Technology | Anti-Malware |
| Audio Analytics | Disaster Preparedness | ID Management |
| Thermal/Infrared Camera | Mass Notification System | Fire & Safety |
| Metal/Weapon Detection | Rescue Operations | Critical Infrastructure |
| License Plate Recognition | Detection Products | And Many Others! |
Don’t see a Direct Hit for your Product, Agency or Organization?
Submit your category recommendation for consideration to Michael Madsen, AST Publisher at: mmadsen@americansecuritytoday.com.
2018 Champions Edition
 See the 2018 ‘ASTORS’ Champions Edition – ‘Best Products of 2018 ‘ Year in Review’ for in-depth coverage of the outstanding products and services of firms receiving American Security Today’s 2018‘ASTORS’ Homeland Security Awards.’
See the 2018 ‘ASTORS’ Champions Edition – ‘Best Products of 2018 ‘ Year in Review’ for in-depth coverage of the outstanding products and services of firms receiving American Security Today’s 2018‘ASTORS’ Homeland Security Awards.’
Enter Early to Maximize Media Coverage of your Products and Services at Kickoff, and Get the Recognition Your Organization Deserves!
And be sure to Register Early for the 2019 ‘ASTORS’ Awards Presentation Luncheon at ISC East 2019 to ensure your place at this limited- space event!